Do Night Vision Goggles Work in Total Darkness and Why?
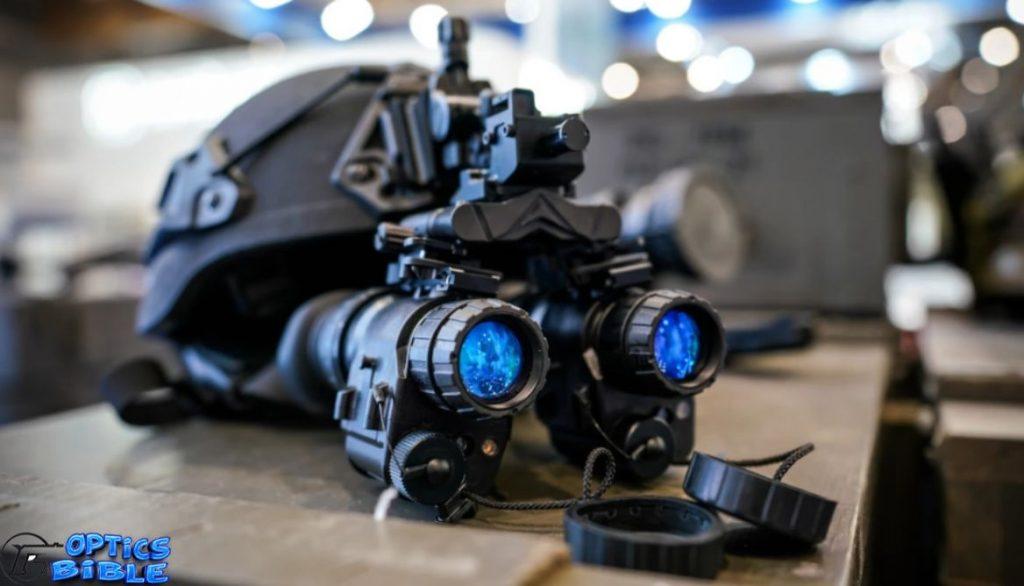

Identifying the target in the darkest hour of the night is the goal of every shooter. One of the perfect tools to achieve this is night vision goggles. However, do night vision goggles work in total darkness?
We will help you answer that with the right facts. Besides that, you will understand night vision technology, how night vision goggles work, and the facts and fiction about night vision devices.
Lets dive into it.
Do Night Vision Goggles Work In Total Darkness?

Night vision goggles are perfect devices in dark situations and particularly in movies and films. They have proved to be very effective on cloudy, moonless nights, The best night vision goggles have the capability of helping people see over 150 meters away.
But, how do night vision goggles work in total darkness? There are different night vision technologies that help make this possible. They include: thermal imaging, active illumination and image intensification.
We will help you understand what they entail and answer some of your burning questions.
General Night Vision Technology
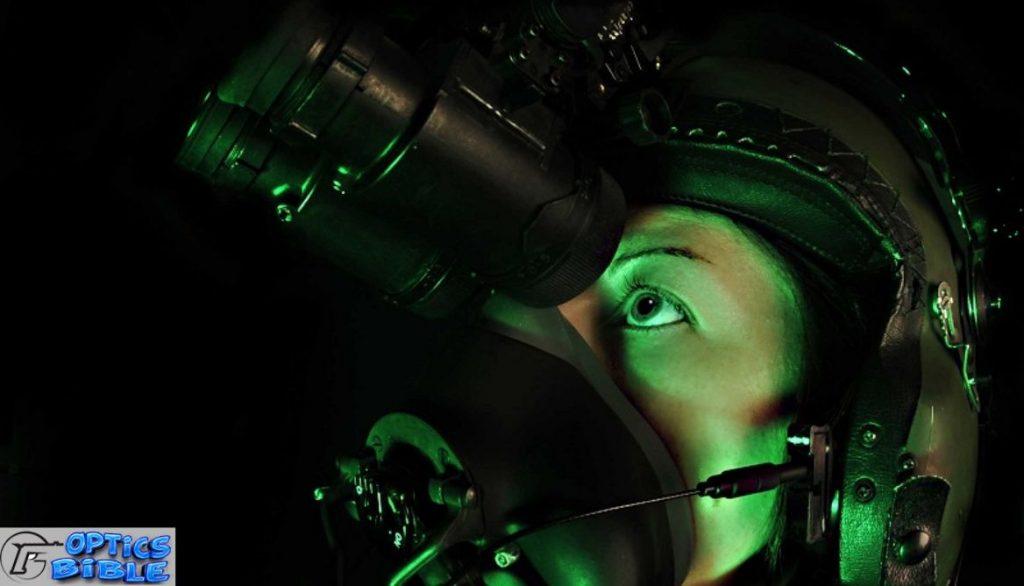

Night vision technology is a type of technology that allows users to see in the dark. This technology is accomplished by using special sensors that detect and amplify low-light levels.
This device then projects an image onto a screen or eyepiece, which allows the user to see in the dark.
There are three key components one looks for in night vision goggles.
- Quality of the night vision tube – This is the most important aspect. Night vision goggles range from Gen 1 to the brightest and clearest Gen 3. This will help you determine the price range of the night vision device.
- The device’s format – Night vision goggles can be binocular with two tubes and two view finders, binocular with a single Nv tube but dual view finders, and monocular with a single NV tube and single viewfinder.
- Weight of the unit: Since night vision goggles for hunting are worn as a headset, This makes it comfortable.
There are three main types of Night vision technologies which include:
Thermal Imaging
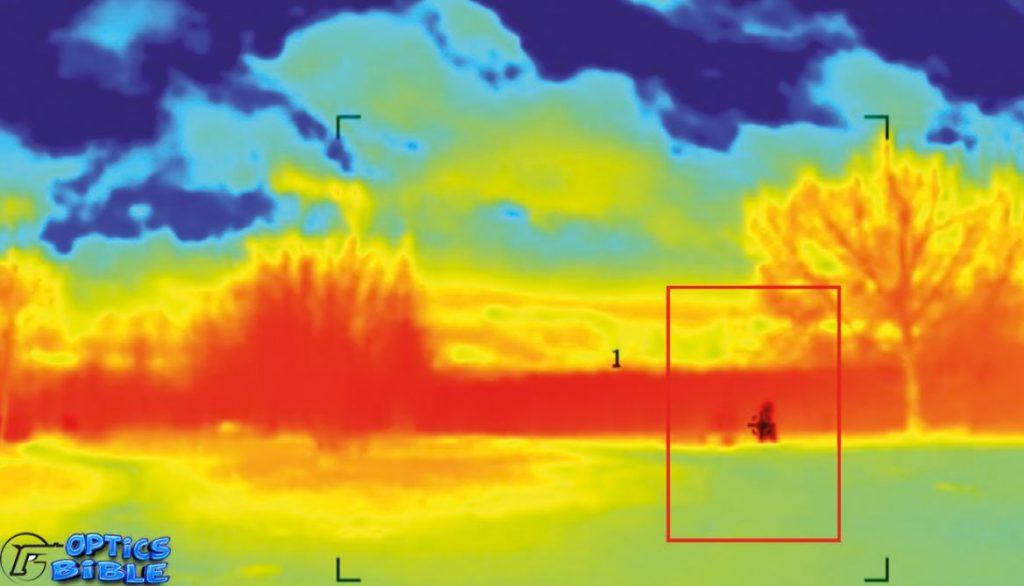
Thermal imaging devices detect the temperature difference between background and foreground objects. It identifies whether a human or animal is in your sight by comparing its temperature to that of nonliving things like rocks and trees.
Thermal imaging cameras are fantastic night vision devices. They detect heat radiation and do not require a Light source. They can see through light fog, rain, and smoke and generate an image even in the darkest of nights (to a certain extent). Thermal imaging cameras can detect minor temperature variations.
How a thermal imaging device works:
- A special lens focuses on the infrared light emitted by all objects in view.
- A phased array of infrared-detector components scans the concentrated light. The detector elements generate a thermogram: a highly detailed temperature pattern. And obtains temperature information for the thermogram in around one-thirtieth of a second. This data is gathered from thousands of places in the detector array’s view area.
- The detector elements’ thermogram is converted into electric impulses.
- The impulses are routed to a signal-processing unit, a circuit board equipped with a specific chip that converts the information from the components into data for the display.
- The information is sent to the display by the signal-processing unit, where it appears in various colors depending on the strength of the infrared emission. The image is created by combining all of the constituents’ impulses.
Thermal imaging equipment is classified into two kinds.
The first is the uncooled version. It is the most prevalent sort of gadget. It works fine at normal room temperature. It is silent, which means it makes no noise when functioning. Activates immediately and has the battery built right in.
The second category is the cryogenically cooled one. It is also more prone to damage from hard handling. This system’s components are contained within a container chilled to 0 degrees Celsius! It has the highest resolution and sensitivity due to the cooling of the components. From a distance of 300m, it can detect a temperature difference of roughly 0.1 degrees Celsius.
Active Illumination

Active illumination is also one of the most inexpensive types of night vision technology, which is why it has many applications for many uses.
Active infrared night vision combines infrared illumination of spectral range 700–1,000 nm (just over the visible spectrum of the human eye) with CCD cameras sensitive to this light. The resulting scene, apparently dark to a human observer, appears as a monochrome image on a normal display device.
One of the best examples of active illumination is the low-light camera.
Laser range gated imaging is another form of active night vision that utilizes a high-powered pulsed light source for illumination and imaging.
The range gating technique controls the laser pulses in conjunction with the shutter speed of the camera’s detectors. Gated imaging technology can be divided into a single shot, where the detector captures the image from a single light pulse, and multi-shot, where the detector integrates the light pulses from multiple shots to form an image.
The lighting technique employed by night vision gadgets is incomparable to that of a standard Light bulb. The light used by night vision systems is near the infrared spectrum.
All objects reflect infrared light from sources like the moon or the stars, and analog night vision devices enhance this light. This typically results in a bright green image thanks to the green phosphor used in their image intensification tubes.
The most common specialty of active illumination night vision technology is the ability to provide a wide range of high visibility even when used in places with heavy snowfall, foggy situations, smokey areas, heavy rainfall, and even misty regions.
This light often illuminates items by reflecting off of them. This also emits a small amount of light to the surrounding surroundings, allowing any night vision equipment you may be utilized to capture and enhance the image.
Image Intensification
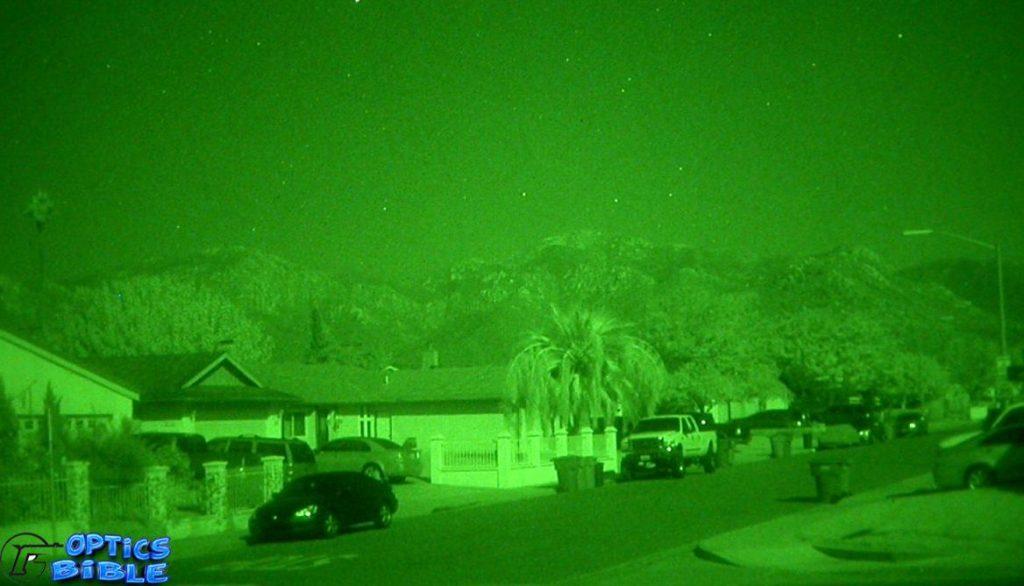

Night vision technology uses the image intensifier tube, commonly known as a vacuum tube. The gadget transforms and magnifies infrared radiation from various natural sources, such as the moon or star, into visible light. The acquired light is brighter than the source light and may be seen with the naked eye.
- The objective lens collects natural sources of ambient Light and near-infrared Light.
- The acquired light is transmitted to an image intensifier tube. The tube then emits around 5,000 volts, which is extremely high for the picture tube’s components.
- This picture intensifier tube transforms light into electrons using its remarkable photo-cathode component.
- As electrons flow through the microchannels, hundreds of more electrons are emitted in each channel. They smash with the channel wall and excite the atoms, resulting in the release of electrons and the initiation of a chain reaction.
- The energy of the electrons drives the phosphors to emit photons. The night vision equipment then displays a green picture on their screens.
The output image is called intensified as this is brighter than the incoming light.
Some of the Pros and cons of image enhancement include the following:
Why Thermal Imaging Devices Help You See Better In Complete Darkness

No Light is Required
This passive technology is particularly stealthy and adaptable because it is utilized in total darkness without illumination. In contrast to infrared night vision goggles, which require some light in their surroundings to function correctly, imaging goggles do not require ambient light and can be used in total darkness.
When You Turn on the Lights While Wearing Night Vision Goggles, Bright light sources cause the IIT to be overwhelmed by photons, and the result is an incredibly bright image with effects often referred to as blooming; this causes vision sensitivity, no usable image, and the automatic shutdown of the goggles.
Continual Coverage 24 Hours a Day –
The image quality of a visible camera is highly dependent on the lighting conditions. In low-contrast or high-dynamic-range environments, the camera may as well not exist. However, thermal imaging is unaffected by ambient light and can be used for continuous day and night monitoring regardless of the time of day.
Ability to Detect Objects in Light or Smoke Fog – Several apparent obscurants, such as smoke, dust, light fog, and light vegetation, allow thermal energy to pass unimpeded. Thermal imaging goggles can see through total darkness and weather obstructions as long as the slightest amount of thermal activity is present.
In addition, because of the precise temperature variations that thermal imaging detects, it can sometimes reveal objects underlying the surface of other materials, such as joists behind a wall or items under clothing.
United States armed forces use thermal imaging devices to scan a general area and acquire a target.
What About Image Clarity In Thermal Images?
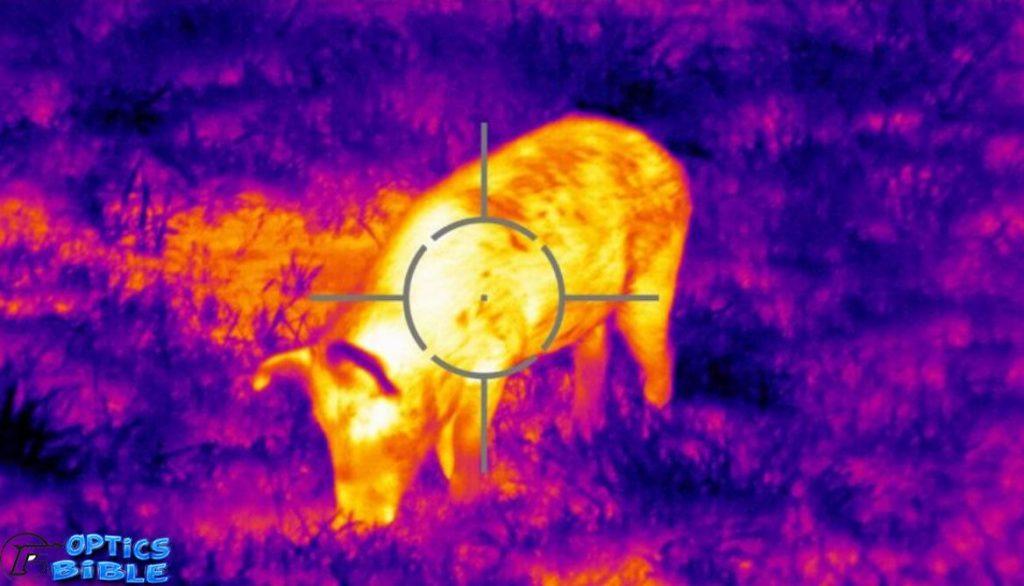

Instead of using light reflected from surfaces to create an image, thermal imaging systems create an image based on the differences in heat between the various objects in the image.
With sufficient light, your photographs will be full of details and shadows. In addition, it will reveal trace heat signatures.
For instance, if you see someone through a thermal imaging device and touch a surface, their handprint will remain on the surface for some time.
To get image clarity for thermal imagers, you must seek a design that balances the display’s image processing, resolution, and brightness to provide image clarity that reveals details.
Here are several techniques for enhancing the sharpness of thermal images:
- Focus – The accuracy of the temperature readings you obtain with an infrared camera depends on your ability to focus the camera. Choose a fixed, manual, or automatic method of focusing that functions well for the average distance to the target at which you conduct checks.
- Optics – Germanium, with its unique coatings, is the most effective optical material for transporting energy to the detector, and it is utilized in the lenses of high-end infrared cameras.
- Detector resolution (pixels) – Each pixel detects the perceived temperature of the target. The greater the number of detector pixels trained on the target, the clearer the image and the more accurate the reading.
- Spatial Resolution – For infrared images, detector resolution and field of view (FOV) are both essential aspects; spatial resolution is sometimes used as a proxy when characterizing the smallest detected object size. Lower spatial resolution levels can produce greater detail and quality images.
Why Does Everything Look Green through Night Vision?

It’s because green is the color most easily perceived by the human eye. The phosphor used to create the image intensifier screen gives night vision scopes their characteristic green hue.
This material is employed because of its luminescent properties; a vivid green glow is produced when electrons collide with the screen. Microchannels on a disc with millions of them carry the electrons through the tube. Voltage surges colliding with these microchannels accelerate motion, producing thick electronic clouds that enhance the original image.
Eventually, these electrons will crash into a phosphorus-coated screen near the tube’s exit. The electrons’ kinetic energy causes the internal display to show a bluish-green hue. Phosphorus in its green form is employed because our eyes can better discern green hues than any other color.
Green phosphors are used in night vision equipment because the human eye can detect more gradients of green than any other color. In addition, green displays are more comfortable to gaze at for extended periods than their black and white counterparts.
How Do Night Vision Goggles Work?
The main component in an NVD is the image intensifier tube (IIT). Multiple components in an IIT allow you to see in the dark.
Primary components include a photocathode, microchannel plate (MCP), phosphor screen, and an eyepiece.
Light is comprised of photons.
Here is a quick look at what night vision binoculars look like and how it functions
Dim Light from a night scene enters the front lens through the objective lens.
- As the photons enter the googles, they strike the photocathode, which is a light-sensitive surface that is a bit like a solar panel that is very precise. Its function is to convert photons into electrons which are then released.
- The electrons are directed toward the microchannel plate. They are then amplified by the photomultiplier, which is a kind of photoelectric cell. Each electron entering the photomultiplier causes more electrons to leave it.
- The electrons leaving the photomultiplier hit the phosphor screen, similar to an old-fashioned television screen. The electrons create tiny flashes of light as they hit the phosphor.
- The photons are then focused by the eyepiece allowing the user to view a recreated scene image.
You can check how the night vision works here.
Fact or Fiction? Common Night Vision Goggle Complaints

Goggles are Heavy
Goggles should be lightweight enough to mount to your helmet comfortably. Unfortunately, they haven’t always been,
The night vision goggles are still heavier compared to a lighter-than-one-pound monocular. Waiting for manufacturers to keep up with the ultra-lightweight trend is a work in progress.
Some night vision goggles weigh up to 40 oz, which burdens the load on your backpack.
Verdict – Fact!
Goggles are Battery Hogs
Carrying spare batteries is another thing to consider and tack onto your person or stash in your pack.
Digital devices are bottomless pits, but image intensifier tubes have better battery life performance, with some lasting as long as 60 hours on a single CR123A or AA battery. However, the night vision goggles lack a built-in rechargeable battery.
Depending on what year you last used night vision goggles or if your only experience is with digital devices, 40-60 hours is pretty good from an IIT.
Verdict – Fiction!
Goggles Need Light
Yes, Night vision goggles work best with some optimal light. You’ll be extremely limited under thick forest canopies or when heavy cloud coverage threatens precipitation of various kinds.
Regardless of the limitations that are out of your control, night vision devices require at least some light, even if it’s minimal. Putting aside the special demands of law enforcement or the military, use an IR illuminator – it’ll do you wonders. Since we all know that night vision isn’t thermal, there’s no point in complaining about its inherent capabilities.
Verdict – Fact!
Non-operable in Unnatural Light
Yes, light can affect night vision Goggles. Night vision goggles work best if there is some ambient light, such as moonlight or starlight. The IR illuminators provide artificial light in the dark but are invisible to the human eye.
The sun is natural, but it’ll destroy your night vision goggles. Analog night vision goggles will suffer damage if exposed to direct sunlight. By contrast, digital night vision goggles work in any lighting condition.
Damage can occur from very bright artificial light too. It would have to be extreme because the most people get from bright light sources like car lights, streetlights, flashlights, etc., is a blooming and washing-out effect. This causes you to lose contrast, sharpness, and usable details for identification.
However, the best night vision goggles come with tubes that can handle and mitigate the effects of bright lights. Some have auto-gating and unfilmed/filmless features to prevent these annoying drawbacks to bright Light sources.
Since there are many Night vision devices with high-performance tubes to help deal with these issues,
Verdict – Fact!
How Else Can Humans See in the Dark?
You might be wondering how else people can see in the dark without night vision goggles. planes and ships use a combination of tools and sensors, which help their navigation.
Things like radar, which uses radio waves to see, sonar, which uses sound to navigate, and GPS are all different types of technologies that can help us work around the fact that we can’t see very well at night.
Besides night vision goggles and thermal imaging devices, the handy flashlight may help us see in low light conditions. Simply shining a bright light on specific objects allows light photons to bounce off them and enter our retinas, mimicking our experience of seeing them in daylight.
FAQ
Does night vision work without any light?
No, Night vision goggles work by enhancing available light sources. Night vision does not work without any light. Night vision is the ability to see in low-light conditions and is made possible by a combination of several physiological adaptations. Rod cells in the retina are sensitive to dim light, while cone cells require light for vision.
The pupils also dilate in dim light to allow light into the eye. Finally, the brain interprets the signals from the rods and cones to create an image. All forms of shape and motion will disappear without a light source, rendering your eyes useless. You would perceive this absence of light as complete blackness.
However, With the proper night-vision gear, you can see a person standing over 180 m away on a moonless,
cloudy night!
Can infrared see in complete darkness?
Yes, Infrared Light has a longer wavelength and lower frequency than regular visible Light. But it can be positioned under darkness. Infrared measures the heat coming from objects in the area, which can be read by the camera, even if no light is required.
When light is available, infrared cameras will give you a color picture. If it gets darker, the camera has an IR cut that automatically switches to infrared mode; then, pictures become black and white.
Can you use night vision in a dark room?
Some night vision goggles work on thermal energy and can work well in total darkness since they register the heat energy from different sources around the camera.
Can night vision goggles see through walls?
No, night vision goggles and thermal imaging devices don’t allow for detection past or through walls. Obstructions such as walls, trees, houses, smoke, fog, rain, snow, etc., will impair night vision performance.
There are two common types of “night vision” equipment. The first is called a light amplification or “starlight” scope. The other is called “thermal imaging.”
Light amplification will not allow a user to see through walls, however. Visible light can’t pass through solid, opaque objects because it uses the visible Light spectrum. To theoretically be able to “see through walls,” one must use thermal imaging.
Can night vision see through concrete?
No, this is almost impossible. Night vision devices detect an object’s temperature and infrared wavelengths to see through. Besides this, these devices cannot see through thicker objects where; concrete is one of them.
Thermal cameras employ the heat energy emitted from an object to see through objects. This means they can’t see through thick objects such as concrete, plastic, walls, and many others.
Conclusion
Now you understand how night vision goggles work and what it means for your intended applications.
Have you used night vision goggles before? What was your experience? Share the experience in the comment section below, and remember to share the post with your friends.

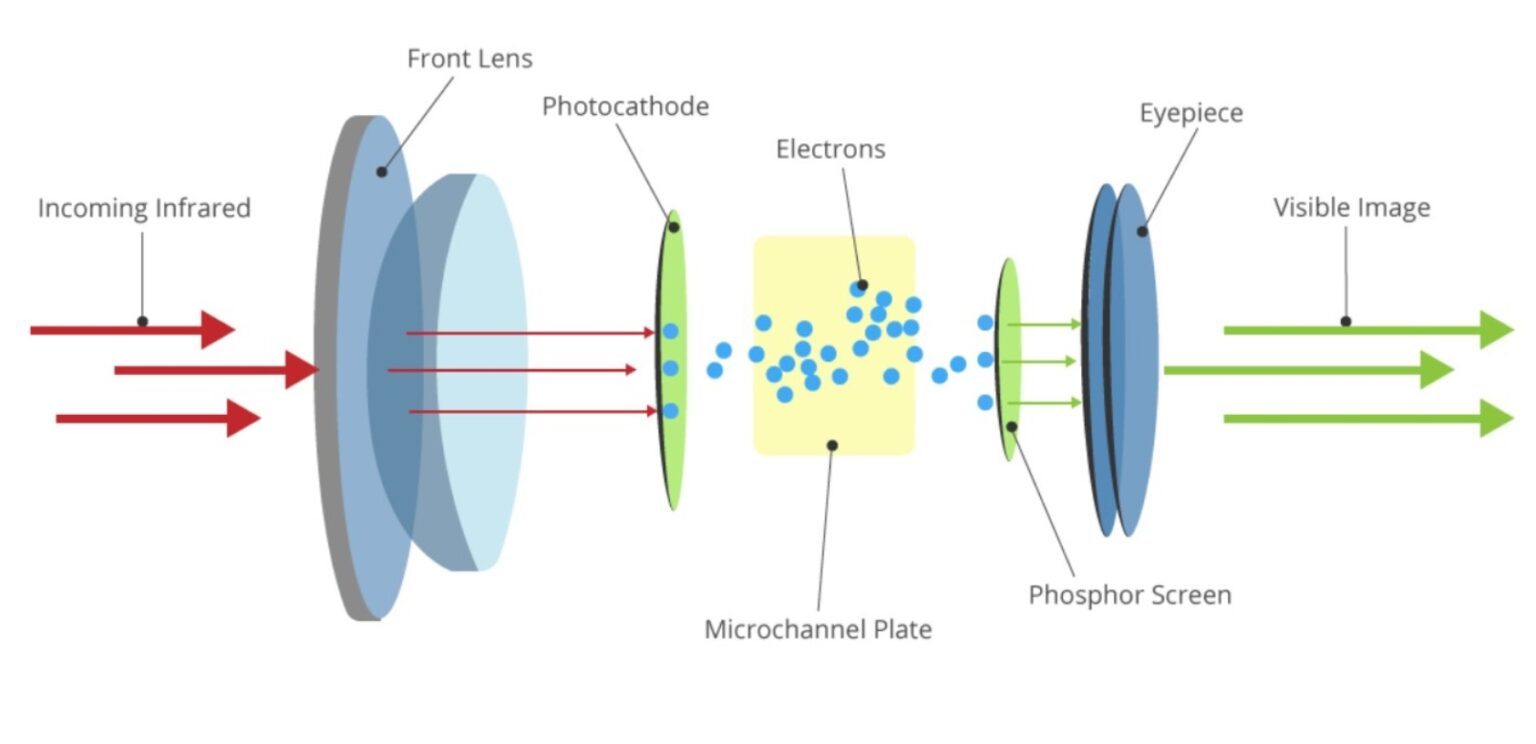 Dim Light from a night scene enters the front lens through the objective lens.
Dim Light from a night scene enters the front lens through the objective lens.